In today’s world, where climate change poses one of our greatest challenges, understanding and reducing our environmental impact has never been more critical. At the heart of sustainable action lies the concept of the carbon footprint. By measuring our carbon emissions, whether as individuals, businesses, or entire communities, we lay the groundwork for impactful change. This article explores what a carbon footprint is, how it can be measured, and why it serves as a fundamental step toward achieving a sustainable future.

Understanding the Carbon Footprint
A carbon footprint represents the total amount of greenhouse gases—primarily carbon dioxide (CO₂)—emitted directly or indirectly by activities such as transportation, energy consumption, and production processes. This measure isn’t confined to a single source; it includes everything from the fuel burned in our vehicles to the energy powering our homes and offices. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) “Tracking these emissions provides a comprehensive picture of our impact on the planet and highlights areas where improvements are possible.”
At its core, the carbon footprint is a metric. It converts a variety of greenhouse gases into a common unit called carbon dioxide equivalents (CO₂e), which allows us to assess the cumulative impact of different gases on global warming. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) emphasizes that “Accurate measurement of these emissions is crucial for developing effective climate policies and strategies.”
The Importance of Measuring Carbon Footprints
Measuring carbon footprints is more than a numbers game—it’s a vital tool for accountability and progress. For individuals, it provides insight into daily habits that contribute to climate change, empowering them to make more sustainable choices. For businesses, understanding the carbon footprint is the first step toward creating strategies that reduce emissions, drive efficiency, and enhance corporate social responsibility.
By quantifying emissions, organizations can:
- Benchmark Performance: Establish baseline metrics and monitor improvements over time.
- Identify Reduction Opportunities: Pinpoint high-impact areas where investments in efficiency or renewable energy can yield significant benefits.
- Enhance Transparency: Build trust with stakeholders by publicly sharing progress toward sustainability goals.
Ultimately, measuring carbon footprints fosters a culture of responsibility and continuous improvement, paving the way for sustainable impact across all levels of society.
Methodologies for Measuring Carbon Footprints
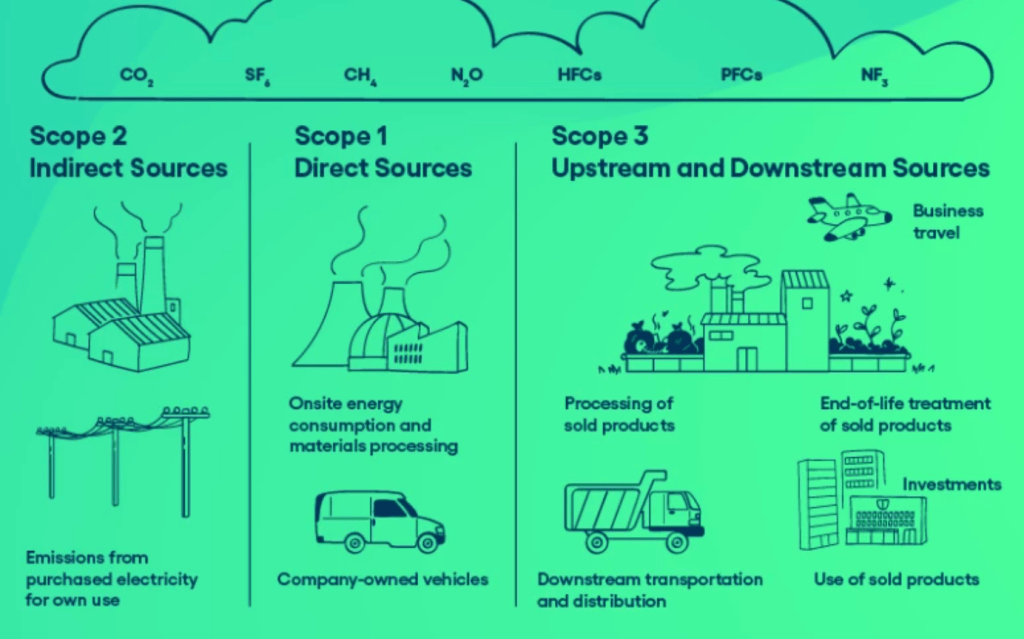
Several methodologies have emerged to help standardize the process of measuring carbon emissions. One of the most widely used frameworks is the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol, developed by the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD). This protocol categorizes emissions into three scopes:
- Scope 1: Direct emissions from owned or controlled sources.
- Scope 2: Indirect emissions from the generation of purchased energy.
- Scope 3: Other indirect emissions, such as those associated with the supply chain or product use.
Another approach is the Life Cycle Analysis (LCA), which assesses environmental impacts associated with all the stages of a product’s life—from raw material extraction through production, use, and disposal. LCA is especially useful for understanding the broader impacts of products and services beyond immediate energy consumption.
Tools and Technologies
As technology advances, so to do the methods for measuring and reducing carbon footprints. Today, a range of tools—from simple online calculators to sophisticated enterprise software—can help track emissions in real time. For instance:
- Online Carbon Calculators: Many organizations, including the EPA, offer user-friendly tools that allow individuals and small businesses to estimate their carbon footprint based on energy usage, travel habits, and consumption patterns.
- Enterprise Solutions: Large companies often rely on integrated software platforms that consolidate data from various operations, enabling a comprehensive overview of emissions across all scopes.
- Remote Sensing and IoT Devices: Emerging technologies such as satellite imagery and Internet-of-Things (IoT) sensors provide granular data that can refine emission estimates and monitor changes over time.
Certification bodies like Gold Standard and Verra further ensure that carbon reduction projects meet rigorous criteria. Their verified carbon credits are backed by meticulous monitoring and third-party audits, ensuring that each credit represents a genuine reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Benefits and Challenges
The benefits of measuring carbon footprints are multifaceted. On the positive side, quantifying emissions provides a clear roadmap for sustainability. It drives innovation by highlighting areas for improvement and encouraging investments in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable practices. Moreover, the transparency that comes from accurate measurement helps build consumer trust and fosters a culture of accountability.
However, there are challenges as well. Data collection can be complex, particularly when trying to account for Scope 3 emissions, which often involve multiple stakeholders across a supply chain. Additionally, variations in measurement standards can lead to inconsistencies, complicating the comparison of emissions data between different organizations. Despite these challenges, the benefits of accurate measurement far outweigh the hurdles, as they provide the essential insights needed to drive effective environmental strategies.
The Path to Sustainable Impact
Measuring your carbon footprint is the essential first step toward sustainability. For businesses, it sparks initiatives that reduce environmental impact, drive innovation, cut costs, and boost competitiveness. For individuals, it inspires lifestyle changes for a healthier planet. By managing emissions, you also unlock the potential of carbon credits—offsetting unavoidable emissions through projects that actively reduce greenhouse gases. This combined approach accelerates the transition to a low-carbon economy, a goal increasingly vital under global agreements like the Paris Agreement.
Conclusion
Accurate carbon footprint measurement is a powerful tool for climate action. Whether you’re an individual or a business, adopting standardized methods and leveraging advanced technologies empowers you to make impactful decisions. At Offset Flow, we believe that knowledge is the catalyst for change—every ton of CO₂ saved brings us closer to a sustainable future.
Are you interested in calculating your carbon footprint? Contact us here: SOLUTIONS.

References and Further Reading
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). (n.d.). Carbon Footprint Calculator. Retrieved from https://www.epa.gov/
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). (2018). Global Warming of 1.5°C. Retrieved from https://www.ipcc.ch/
- Greenhouse Gas Protocol. (n.d.). The GHG Protocol Corporate Standard. Retrieved from https://ghgprotocol.org/
- Gold Standard. (n.d.). Project Certification for Carbon Credits. Retrieved from https://www.goldstandard.org/
- Verra. (n.d.). Verified Carbon Standard (VCS). Retrieved from https://verra.org/
Offset Flow
Carbon Credits & Net-Zero. TOGETHER.
Menú









